Classification
Cell Staining
Introduction
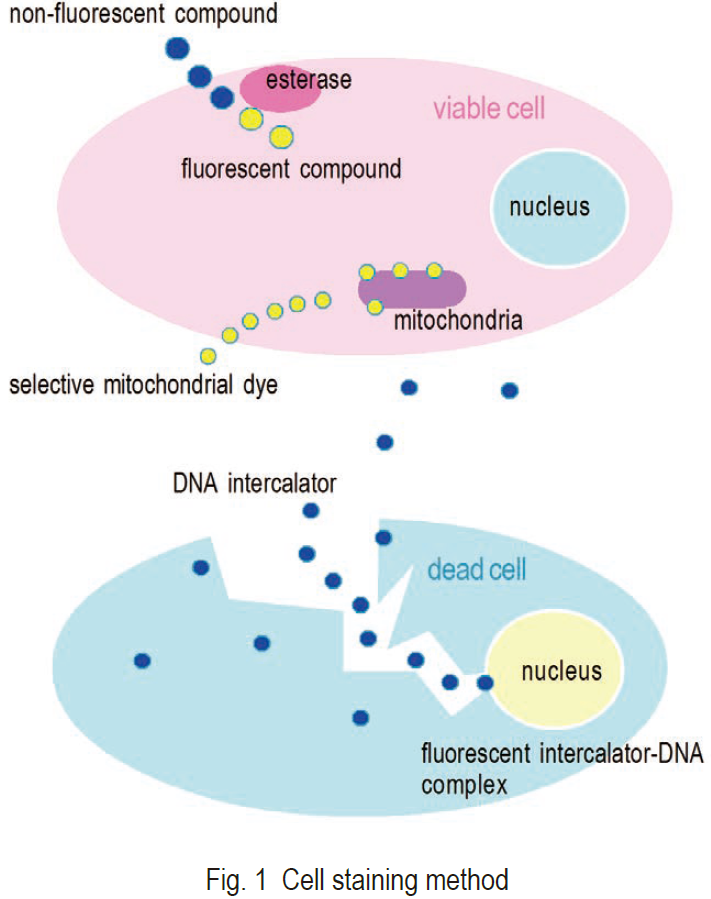 Visualization of a cell with fluorescent compounds provides a wide variety of information for the analysis of cell functions. Various activities and structures of a cell can be targeted for staining with fluorescent compounds (Fig. 1). The most commonly stained cell components are cell membranes, proteins, and nucleotides. Small neutral molecules and positively charged molecules can pass through viable cell membranes and remain inside of cells, depending on their reactivity or hydrophilicity. Negatively charged molecules cannot pass through viable cell membranes. Positively charged molecules are usually cell membrane permeable and accumulate in mitochondria. Ester is a suitable functional group for staining viable cells. Ester can pass through viable cell membranes, where it is hydrolyzed by cellular esterases into a negatively charged molecule under physiological conditions. Several fluorescein analogs with ester groups in their structure are available for staining viable cells. Succinimidyl ester compounds can also be used to improve retention of the fluorescent derivative within the cell. These compounds are neutral molecules that pass through cell membranes and covalently conjugate with cell proteins. Covalently conjugated molecules can stay in the cell for several weeks. Nucleotide staining with fluorescent intercalators is mostly used for dead cell detection.
Visualization of a cell with fluorescent compounds provides a wide variety of information for the analysis of cell functions. Various activities and structures of a cell can be targeted for staining with fluorescent compounds (Fig. 1). The most commonly stained cell components are cell membranes, proteins, and nucleotides. Small neutral molecules and positively charged molecules can pass through viable cell membranes and remain inside of cells, depending on their reactivity or hydrophilicity. Negatively charged molecules cannot pass through viable cell membranes. Positively charged molecules are usually cell membrane permeable and accumulate in mitochondria. Ester is a suitable functional group for staining viable cells. Ester can pass through viable cell membranes, where it is hydrolyzed by cellular esterases into a negatively charged molecule under physiological conditions. Several fluorescein analogs with ester groups in their structure are available for staining viable cells. Succinimidyl ester compounds can also be used to improve retention of the fluorescent derivative within the cell. These compounds are neutral molecules that pass through cell membranes and covalently conjugate with cell proteins. Covalently conjugated molecules can stay in the cell for several weeks. Nucleotide staining with fluorescent intercalators is mostly used for dead cell detection.
Cell Cytosol Staining
Fluorogenic esterase substrates that can be passively loaded into viable cells, such as Calcein-AM, BCECFAM, Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE), and Fluorescein diacetate (FDA), are converted by intracellular esterases into fluorescein analogs with green fluorescence. Calcein and BCECF can be converted into electrically neutral molecules by the addition of acetyl or acetoxymethyl groups to their phenolic OH or carboxylic groups, which allows them to freely permeate into the cell. Once converted into fluorescent products by esterase, these compounds are retained by cells because of their negative charges. These esterase substrates, therefore, can serve as assay probes of cell viability. Fluorescent esterase substrates may also be used in cell viability assays in place of tetrazolium analogs such as MTT or WST. The mechanism for determining cell viability is different: Although both assays determine cell metabolism, esterase substrates detect esterase activity; tetrazolium salts detect dehydrogenase activity of viable cells. CFSE is also an ester compound that passes through viable cell membranes. Since it has an amine-reactive succinimidyl group, fluorescein derived from CFSE can covalently bond to proteins or other amino groups in the cell or on the cell membrane. This covalently attached fluorescein remains stable and allows the cell to be traced over several weeks.
Mitochondria Staining
Mitochondria exist in most eukaryotic cells and play a very important role in oxidative metabolism by generating ATP as an energy source. The average number of mitochondria per cell is from 100 to 2,000. Although the typical size is about 0.5-2 mm, the shape, abundance, and location of mitochondria vary by cell type, cell cycle, and cell viability.Therefore, visualization of mitochondra is important. Since mitochondria have electron transport systems, they can be stained with various redox dyes. MitoRed and Rh123 readily pass through cell membranes and accumulate in mitochondria. The fluorescence intensity of Rh123 reflects the amount of ATP generated in mitochondria.
Nucleus Staining
Fluorescent dyes with aromatic amino or guanidine groups, such as propidium iodide (PI), diaminophenylindole (DAPI), acridine orange (AO), and Hoechst dyes, interact with nucleotides to emit fluorescence. PI molecules intercalate inside the DNA double helix. DAPI and Hoechst dye molecules attach at the minor groove of the DNA double helix. On the other hand, AO can form complexes with either double-stranded DNA or single-stranded DNA and RNA. One molecule of AO can intercalate with three base pairs of double-stranded DNA to emit green fluorescence with the maximum wavelength at 526 nm. One molecule of AO can also interact with one phosphate group of single-stranded DNA or RNA to form an aggregated, or stacked, structure that emits red fluorescence with the maximum wavelength at 650 nm. Cell membranes of viable cells are impermeable to these fluorescent dyes,except for the Hoechst dyes, and these dyes can therefore be used as fluorescent indicators of dead cells. Hoechst dyes are positively charged under physiological conditions and can pass through viable cell membranes.
Bacterial Cell Staining
There are several ways to detect bacteria, including agar plate cultivation and bacteria-specific DNA amplification. Fluorescent staining using CTC is another method used to detect viable bacterial cells. The advantage of this method is very quick detection and the possibility of detecting VNC (viable but non-culturable) bacterial cells. CTC is a tetrazolium salt that is converted to formazan dye by bacterial cell activity. The solid state of the formazan dye emits red fluorescence. Therefore, viable bacterial cells can be stained by CTC and are easily detected by fluorescent microscopy.
Product
- Cell Double Staning Kit
-
Code Product name Unit size CS01 Cell Double Staining
-Cellstain®- Double Staining Kit1 set - Live Cell Staining
-
Code Product name Unit size C326 Live Cell Staining
-Cellstain®- Calcein-AM1 mg C375 Live Cell Staining
-Cellstain®- CFSE1 mg C396 Live Cell Staining
-Cellstain®- Calcein-AM solution1 ml C410 Live Cell Staining
-Cellstain®- CytoRed solution1 mL F209 Dead Cell Staining
-Cellstain®- FDA1 mg - Dead Cell Staining
-
Code Product name Unit size D212 Dead Cell Staining
-Cellstain®- DAPI1 mg D523 Dead Cell Staining
-Cellstain?- DAPI solution1 ml P346 Dead Cell Staining
-Cellstain®- PI1 mg P378 Dead Cell Staining
-Cellstain®- PI solution1 ml - Nuclear Staining
-
Code Product name Unit size A430 Nucleus Dye
-Cellstain®- AO solution1 ml H341 Nucleus Dye
-Cellstain®- Hoechst 33258 solution1 ml H342 Nucleus Dye
-Cellstain®- Hoechst 33342 solution1 ml - Mitochondria Staning
-
Code Product name Unit size MD01 Mitophagy Detection
Mitophagy Detection Kit1 set MT05 Mitochondrial Singlet Oxygen Imaging
Si-DMA for Mitochondrial Singlet Oxygen Imaging2 μg MT11 Mitochondrial Staining
MitoBright LT Red20 μl
400 μl
400 μl x 3MT12 Mitochondrial Staining
MitoBright LT Deep Red20 μl
400 μl
400 μl x 3MT13 Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Detection
MT-1 MitoMP Detection Kit1 set MT14 Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection
mtSOX Deep Red - Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection100 nmol R237 Mitochondrial Staining
-Cellstain®- MitoRed50 μg x8 - Tissue Staining
- Nucleolus Staining
-
Code Product name Unit size N511 Nucleolus Fluorescent Staining
Nucleolus Bright Green60 nmol N512 Nucleolus Fluorescent Staining
Nucleolus Bright Red60 nmol - Lipid Droplet Staining
-
Code Product name Unit size LD01 Lipid Droplet Staining
Lipi-Blue10 nmol ※ LD02 Lipid Droplet Staining
Lipi-Green10 nmol ※ LD03 Lipid Droplet Staining
Lipi-Red10 nmol ※ LD04 Lipid Droplet Staining
Lipi-Deep Red10 nmol ※ LD05 Lipid Droplet Assay
Lipid Droplet Assay Kit - Blue1 set ※ LD06 Lipid Droplet Assay
Lipid Droplet Assay Kit - Deep Red1 set ※ - Cell Membrane Staining
-
Code Product name Unit size P504 Cell Membrane Staining
PlasMem Bright Green100 μl P505 Cell Membrane Staining
PlasMem Bright Red100 μl - Lysosome Staining
-
Code Product name Unit size L261 Lysosome Staining Dye Green
LysoPrime Green - High Specificity and pH Resistance10 µl
10 µl x 3L264 Lysosome Staining Deep Red
LysoPrime Deep Red - High Specificity and pH Resistance1 tube
3 tubesL265 Lysosomal pH Detection Reagent Red
pHLys Red - Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection1 tube
3 tubesL266 Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit
Lysosomal Acidic pH Detection Kit1 set